Low energy availability is a condition that occurs when an individual’s energy intake falls short of their energy expenditure, resulting in an insufficient amount of energy to support all physiological functions required for optimal health, putting the body in a complex state. LEA is often used interchangeably with Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S), which is a broader syndrome that highlights the negative health consequences of chronic low energy availability in multiple organ systems in athletes due to exercise. Both LEA & RED-S can affect both male and female at all ages.
A good analogy to illustrate LEA is when your mobile phone’s battery is low, and its screen starts to dim while background apps shut down to conserve energy. The body enters a mode of energy conservation, downregulating certain body functions and even shutting down others to conserve energy. This is akin to putting your phone in power-saving mode to extend its battery life.
How can LEA be caused?
Low energy availability can either occur intentionally, or unintentionally.
Intentional:
Reducing your caloric intake and or increasing training intensity and /or volume for various reasons, including those related to performance goals such as making weight in weight-class or physique-focused sports like gymnastics or MMA. These behaviors can affect your relationship with food, potentially leading to psychological issues such as anxiety, depression, and eating disorders.
Another reason to excessive calorie restriction could be diagnosed eating disorders e.g., binging and/ or over exercising. Something else to consider is disordered eating behaviors. Although these are not as extreme as eating disorders, they can contribute to LEA. Examples of disordered eating include skipping meals & becoming orthorexic, a condition you have an excessive preoccupation with calorie counting, healthy or “clean” eating, leading to obsessive behaviors and rigid restrictions around food choices.
It is important to note that food tracking and its apps can be extremely beneficial tools to learn about your diet and what is in your food and should not be dismissed as causes of disordered eating/ eating disorders. These disorders have been around before food tracking became popular and are more likely to do with an individual’s relationship with food. Please seek professional help if you are experiencing disordered eating.
Pro-tip: if you are an athlete who regularly uses food tracking apps, it can be good practice to eat innately during off-season where your performance is not going to be affected. It is a good strategy to shake things up and assess how you feel about not tracking.
Unintentional:
Increasing training volume and/or intensity without matching these needs with your dietary intake, often resulting in injuries. This could be due to a lack of time and or organisation to prepare and plan your meals around your training. LEA can also be caused by eliminating foods or food groups to improve your physical appearance or athletic performance, which, if done without appropriate alternative replacements or professional supervision can result in LEA and negatively impact your performance and overall health. Additionally, personal beliefs or preferences, e.g., religious dietary restrictions, pressures, or influences from people around you or social media can influence your eating behaviors which could have an impact on your energy availability state. Tied in with this is the lack of knowledge and understanding of nutrition. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that athletes receive proper guidance and education regarding their nutritional needs to prevent LEA and other negative health outcomes.
Failure to recognise LEA can lead to severe health issues that can affect the ability to practice, compete and impair your health. Below are the signs and symptoms that you should monitor to avoid getting into a LEA state.
Common Signs & Symptoms of LEA
✅ Irregularity/ cessation of the Menstrual cycle
✅ Poor training adaptation
✅ Recurring injury/illnesses e.g., recurring stress fractures
✅ Gut disturbances e.g., bloating, constipation
✅ Sleep disturbances
✅ Low mood/ unmotivated e.g., sadness, frustration, tiredness
It is important to note that not all symptoms will be experienced in a LEA state.
Monitoring and identifying some or all of these signs and symptoms can be key indicators of your body being in a LEA state, and consequently under fueled for optimal health and performance in your given sport.
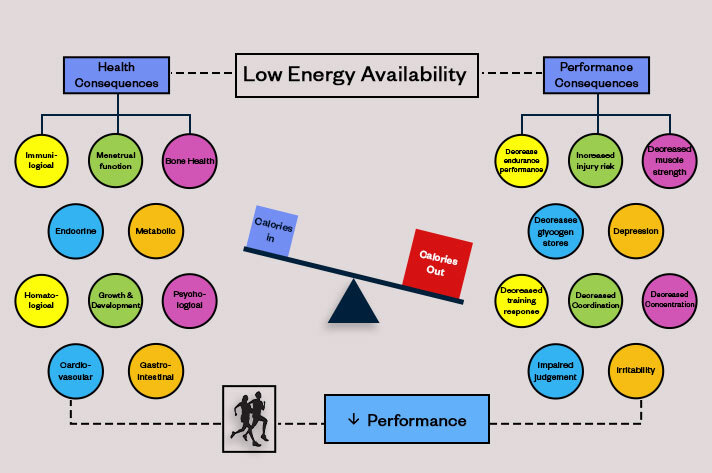
Health Consequences of Being in a LEA State
LEA can affect many body systems as demonstrated below.
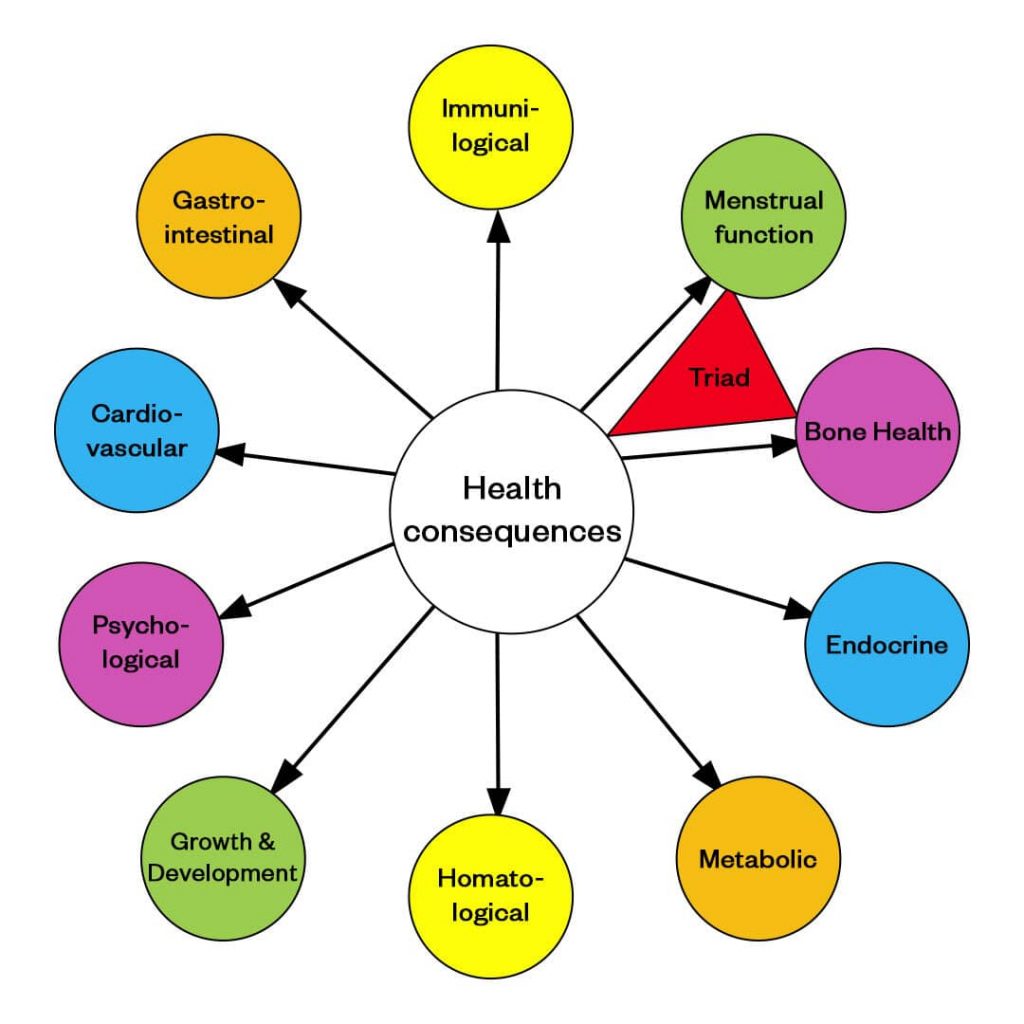
Skeletal System in a LEA state
In a LEA state bone tissue and minerals from the bone are broken down to release energy for other bodily processes, impairing.
• Bone cells and hormones regulation
• Bone growth
• Reshaping of the skeleton into a strong load bearing structure
This can increase susceptibility to bone breaks, bone stress injuries, or stress fractures. This effect can be especially significant in athletes, who have higher bone density requirements due to the physical demands of their sport. This is even more important for women and/ or non-weight bearing sports e.g., cyclists who are at increased risk of osteoporosis.
Endocrine System in a LEA state
In a low energy availability state, there is insufficient energy for:
• Hormone production thus its function e.g., down regulation of estrogen, which affects the reproductive system, preventing menstrual function. Estrogen also plays a role in bone metabolism and a decline in estrogen production can weaken our bones. Increasing risk of osteoporosis and bone fractures. So, a downregulation of the endocrine system also impairs the skeletal and the menstrual system. Another example is downregulation of testosterone which is important for the development and maintenance of bone density and muscle mass.
• Optimal reproductive system function
• Bone metabolism = increasing rise of osteoporosis & bone fractures
• Endocrine system, downregulating it which impairs the skeletal & the menstrual system.
Psychological Function in a LEA State
A low energy availability state can cause:
• Mood changes (bouts of depression)
• Reduced concentration (brain fog)
• Increased irritability
• Anxiety
Severity of Damage
LEA is complex and the severity of the damage caused by being in a LEA state could vary between the body systems. So, it could affect one or multiple body systems at different severities whilst not affecting others. This is likely dependent on which body system is the weakest for the individual based on several factors, e.g., sex, duration and degree of energy restriction, age, training status. For example, young athletes are more susceptible to the negative effects of LEA on growth and development whereas women are more prone to decreased bone density and infertility.
The severity with which body systems are affected depends on the duration and the drop in low energy availability. The larger the drop in energy availability, which could be caused by increased energy deficit and/ or energy expenditure, the more severe the impact is on your affected body systems. Also, the longer you are in a LEA state the more severe the effect is likely to be. So chronic dieters who remain in low energy availability state for lengthy periods of time are more likely to experience the damage of LEA across multiple body systems or experience a higher severity of damage to an individual body system.

Performance Consequences of Being in a LEA State
Below is a diagram demonstrating the consequences of LEA on performance. This includes reduced endurance performance, training response, concentration, coordination, glycogen stores and increased risk of injury.
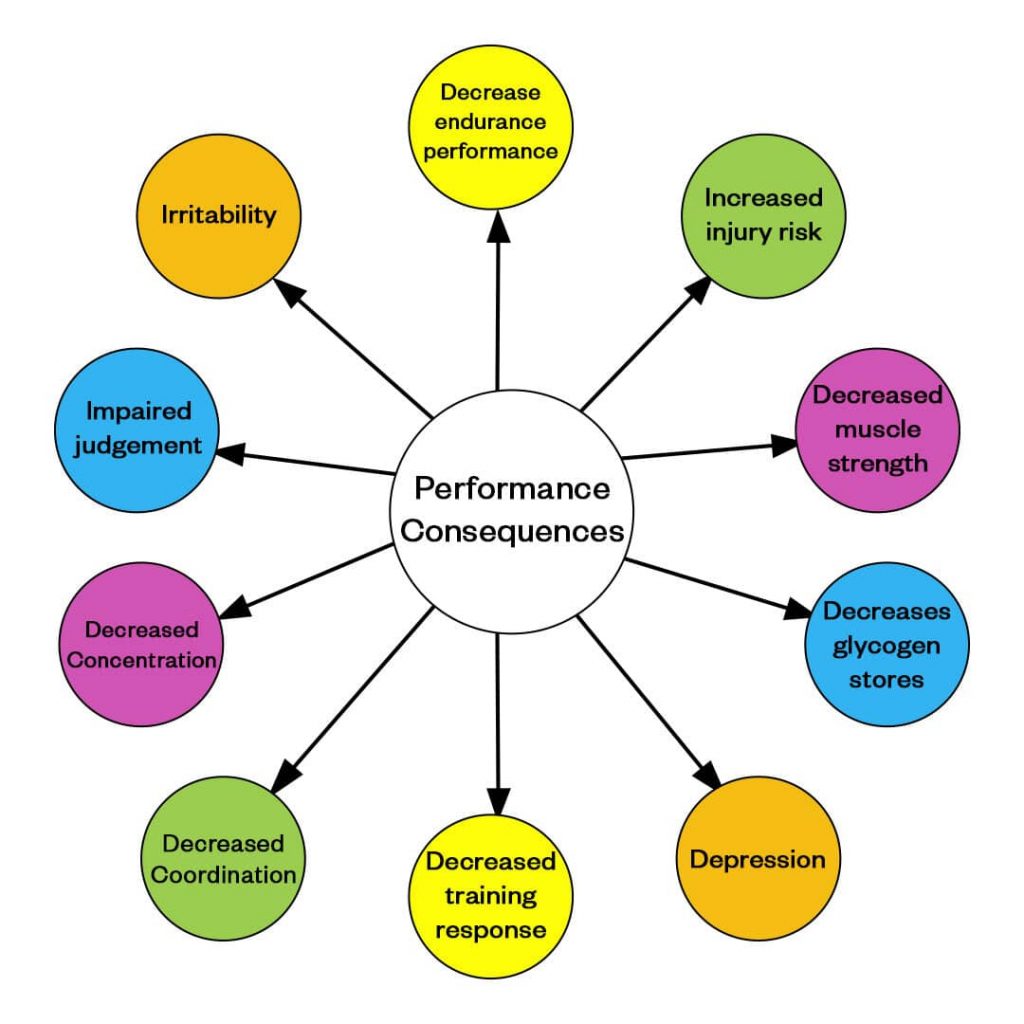
These performance impairments can be observed physically and/ or psychologically.
Neural and Psychological Effects
LEA can reduce your coordination which also ties in with increased risk of injury. And this is because when you have decreased coordination, you are more likely to trip or fall, consequently increasing your injury risk. LEA also causes poor decision making, impairing judgment which is crucial for when quick decisions need to be made, e.g., basketball, football, tennis, martial arts. Split-second decisions can make the difference between winning and losing in these sports, and impaired judgment due to LEA can lead to increased risk of injury and poor performance, reducing the opportunity of success in competition.
Physical Effect of LEA
LEA can reduce muscular strength and endurance which can hinder training adaptations.
LEA is complex and can impair both your health and performance during training and competition. However, if you look out for signs and symptoms by monitoring your body systems this could help you recognize when your body might be in a LEA state, and this is where working with a performance nutritionist on a one-to-one basis would be beneficial.