It’s a Saturday morning and my brother is getting ready for a 10km run in preparation for an upcoming race. My sister is going out for a light run as she wants to lose a few pounds. They both eat the same pre workout breakfast consisting of cereal and fruit juice because they want to have enough energy to get through their run. Both of them see their breakfast as a good pre workout meal.
This sets the tone for every workout session they do, but should they eat the same thing based on their workout? Is it a good performance meal? The simple answer is no.
There are 2 main factors that will help you determine what to eat before a workout. You should consider the following:
- Your goals (performance vs weight management)
- Workout intensity/volume (high vs low/moderate)
Eating the same thing before each workout session could be one reason why you do not see the results you’re after, and that’s because not every workout session is the same.
So why would you eat the same pre-training meal?
What to eat before exercise: Performance meals
To optimise your workout:
•Balanced macronutrients like protein, carbohydrates, and fats help to boost your performance. The timing of nutrient consumption may vary based on individual preferences, digestion speed, and goals.
•Experiment with different nutrient sources and consult a registered sports nutritionist for personalised guidance.
•Remember, providing your body with the proper nutrients before a workout helps to enhance your performance and aid recovery.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are best thing to eat before a workout. They are considered as the king when it comes to performance.To improve performance, fuel your training well with sufficient carbohydrates as they are king for energy. Carbohydrates are a major part of a training diet for athletes. For athletes, carbohydrate-rich meals are the best food to eat before a workout. When carbohydrates are consumed, they are stored in the muscles and liver as glycogen, which is the body’s preferred energy source during high-intensity exercise. So, high-carb foods are usually great pre-workout meals. This is why athletes like marathon runners eat more carbohydrates with each meal to maximise energy availability in the days before a race.
Consuming easy-to-digest carbohydrates that have a low glycaemic index (GI) in the hours before training will also provide a steady release of energy to fuel your workout. As workout intensity and volume increases, so does your body’s requirement for carbohydrate to fuel this type of training. Athletes who train multiple times per day will require more carbohydrates to help them perform at their best and recover after each session.
Protein
Consuming a moderate amount of protein before a workout can benefit athletes and individuals looking to maximise their performance and recovery. Here are a few reasons why including protein before a workout is advantageous:
1. Muscle Protein Synthesis: The amino acids in protein are the building blocks of muscle tissue. Consuming protein before a workout can stimulate the muscle. Muscle protein synthesis is the physiological process for the body to enhance muscle growth, repair, and recovery.
2. Muscle Preservation: The chances of muscle breakdown are high during resistance training or high-intensity workouts. Consuming some protein before and after a workout can help to preserve muscle mass and excessive muscle breakdown.
3. Sustained Energy: Consuming protein alongside carbohydrates before a workout can provide sustained energy. Protein takes longer to digest, so it’s important not to consume this too close to the start of your training as it may cause GI distress.
4. Improved Muscle Performance: Protein consumption before a workout may enhance muscle strength, power, and endurance. It can help optimise muscle function and contribute to better overall athletic performance.
When considering protein before a workout, choosing easily digestible protein sources that won’t cause discomfort during exercise is essential. Some suitable options include:
– Lean meats like chicken or turkey breast
– Fish such as salmon or tuna
– Eggs
– Low fat Greek yogurt or cottage cheese
– Plant-based protein sources like tofu
– Protein shakes or smoothies with whey or plant-based protein powder
The timing of protein consumption before a workout can vary depending on personal preference, digestion speed, and individual goals. Optimal protein intake before a workout varies among individuals. Some prefer protein-rich foods or supplements before 1-3 hours of workout. At the same time, others opt for a smaller snack or shake closer to their workout.
Listening to your body and experimenting with timing and different protein sources is essential. Find out what works best for you regarding energy levels, digestion, and workout performance. Consulting with our registered sports nutritionist will help you to plan your nutrition.
Fat
While carbohydrates are crucial for immediate, high-intensity energy, fats are an effective energy source for low-moderate intensities. Omega 3 rich fish, eggs, nuts, seeds, avocado, and olive oil are sources of healthy fats that can contribute to a steady release of energy, plus many other health benefits.
Fluids
Hydration is vital before exercise to maintain performance and prevent dehydration. Drinking water before and during exercise helps to ensure proper hydration levels and supports overall performance. Other fluids options, like sports drinks or coconut water, are also available to stay hydrated.
Options of food to eat before a workout [ When the workout is performance-focused ]
Optimise performance with proper pre-workout nutrition. Discover a range of foods to eat before your workout to fuel your body and enhance energy levels for effective workouts. Consuming the foods in the appropriate quantities and proper manner is essential to achieve optimal results. These foods are rich in the respective categories mentioned and can fuel your body effectively for improved performance during workouts. For personalised guidance, consider consulting with our nutritionist, who can provide tailored recommendations based on your needs and goals. Their expertise can further support your journey toward optimal nutrition and fitness.
Carbohydrate
1.Grains and Cereals:
- Rice (white, brown, wild)
- Oats
- Quinoa
- Barley
- Wheat (including whole wheat bread and pasta)
- Millet
2.Starchy Vegetables:
- Potatoes and other root vegetables
- Butternut squash
- Peas
- Corn
3.Legumes and Pulses:
- Lentils
- Chickpeas
- Mixed beans
4.Fruits:
- Bananas
- Apples
- Oranges
- Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries)
- Grapes
- Pineapple
- Mangoes
5.Dairy Products:
- Milk
- Yogurt (Greek, SKYr and other varieties)
- Cottage cheese
- Sugary Foods:
- Honey
- Maple syrup
- Jam and jellies
- Sweets
- Soft drinks
- Pastries and dessertsEnergy drinks
Protein
1.Lean Meats:
- Chicken breast
- Turkey breast
- Lean cuts of beef (e.g., sirloin, tenderloin)
- Pork tenderloin
2.Fish and Seafood:
- Salmon
- Tuna
- Trout
- Shrimp
- Cod
- Sardines
3.Eggs and Dairy Products:
- Eggs
- Greek yogurt
- Cottage cheese
- Milk
- Cheeses
4.Legumes and Pulses:
- Lentils
- Chickpeas
- Mixed beans
- Edamame
- Nuts and seeds
5.Soy Products:
- Tofu
- Tempeh
- Soy milk
- Edamame
6.Nuts and Seeds:
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Peanuts
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
- Pumpkin seeds
7.Protein-rich Grains and Cereals:
- Quinoa
- Buckwheat
- Amaranth
- Farro
- Barley
- Oats
8.Plant-based Protein Alternatives:
- Plant-based protein powders (pea protein, soy, hemp protein, etc.)
Seitan - Vegan meat substitutes (tofu-based, tempeh-based, Quorn etc.)
Source Of Fluids
1.Fruits:
- Watermelon
- Oranges
- Pineapple
- Strawberries
- Grapefruit
- Grapes
- Cantaloupe
- Peaches
2.Vegetables:
- Cucumber
- Lettuce
- Celery
- Tomatoes
- Zucchini
- Bell peppers
- Spinach
- Radishes
3.Soups and Broths:
- Clear vegetable or chicken broth
- Gazpacho (cold tomato soup)
- Miso soup
4.Smoothies and Juices:
- Smoothies made with water, milk, or yogurt and blended with fruits and vegetables
- Freshly squeezed fruit juices (e.g., orange, grapefruit)
5.Gelatin and Puddings:
- Gelatin desserts (e.g., Jello)
- Chia seed pudding
- Rice pudding
- Yogurt and Dairy-Based Products:
- Plain yogurt
- Greek yogurt
- Cottage cheese
- Milk (dairy or plant-based)
6.Hydrating Foods:
- Chilled or sliced cucumbers
- Water-rich salads with lettuce, tomatoes, and cucumbers
- Chilled fruits like watermelon or grapes
A good pre-workout meal for weight management
During low-moderate workouts, or even at rest, carbohydrate utilisation becomes less reliant and the body’s fat stores become the preferred energy source. People looking to lose weight should eat on a calorie deficit and their pre-workout meals should have fewer carbohydrates. Using eggs, cottage cheese and yoghurt will be the best pre-workout meal for them. Reducing carbohydrate intake enhances the muscle’s ability to utilise fats for energy, and this can be an effective strategy for promoting training adaptations for endurance athletes, but also for maintaining low body fat levels.
Footballers and other team-sport athletes need good amounts of carbohydrates to fuel fitness specific workouts, but when it comes to technical based sessions, that are typically lower intensity, they do not require the same fuelling. In this case, carbohydrate portions would be reduced in pre-workout nutrition (not removed as small amounts still help brain function) for the technical session, instead focus on protein and vegetables to stay satiated during the session.
Now, although pre-workout nutrition with reduced carbohydrates is good in some circumstances, it’s important to remember that the key to losing weight is energy balance. Knowing what to eat before a workout is important to maintain energy balance. If you want to lose weight, you must be in a caloric deficit (use more energy than you eat), and if you want to increase weight, then you must be in a caloric surplus (eat more energy than you use).
On the other hand, conducting some workout sessions with reduced carbohydrate intake can be an effective strategy for helping you to eat less calories overall. Workout before breakfast may mean you’ve skipped a meal compared to eating before and after, therefore consuming less calories overall. You may also have something light like some yoghurt or a couple of scrambled eggs which will be less calories than a bowl of porridge or pasta.
Best pre-workout breakfast with low carbohydrates for weight loss
- Fasted (train before breakfast)
- Eggs (scrambled, boiled, omelette)
- Greek yoghurt
- Cottage cheese
- Whey protein shake in water
The most important thing though, for weight/fat loss, is to stick to what you prefer and can maintain in the long term, if it helps you to achieve a negative caloric balance. So it’s not just about what you eat in that one meal before, as every meal counts if you want to see results!
Also, Learn about post-workout recovery foods.
Pre-workout nutrition: what, when, and how
- Fuel for the work required – use carbohydrates when you need them to maximise performance and reduce when performance is not the priority to promote training adaptations and body composition.
- Focus on easy-to-digest low-GI carbohydrates before a workout for sustained energy.
- Calories are the #1 factor for weight loss
- Working out with reduced carbohydrate intake can be effective to support fat loss, but if not in a caloric deficit then this will not happen.
- If your sole goal is fat/weight loss then sticks to your preference of workout before or after eating if it helps you train for longer and achieve a negative caloric balance.
- One meal can support training/weight goals but it’s what you do consistently across all meals that will help you achieve your goals.
What is Pre-Workout Nutrition
Pre-workout nutrition is a strategic meal or food consumed at a certain time before you exercise. The food is designed to provide proper nutrients for endurance, energy, and recovery. The only aim is to fuel your body with the necessary nutrients to support your physiques.
A decent pre-workout meal should incorporate a balance between carbs and protein, as well as solid fats. Carbohydrates provide the body with energy, while protein assists with muscle recovery and repair. Healthy fats, like those found in nuts, seeds, and avocados, give supported power all through exercise.
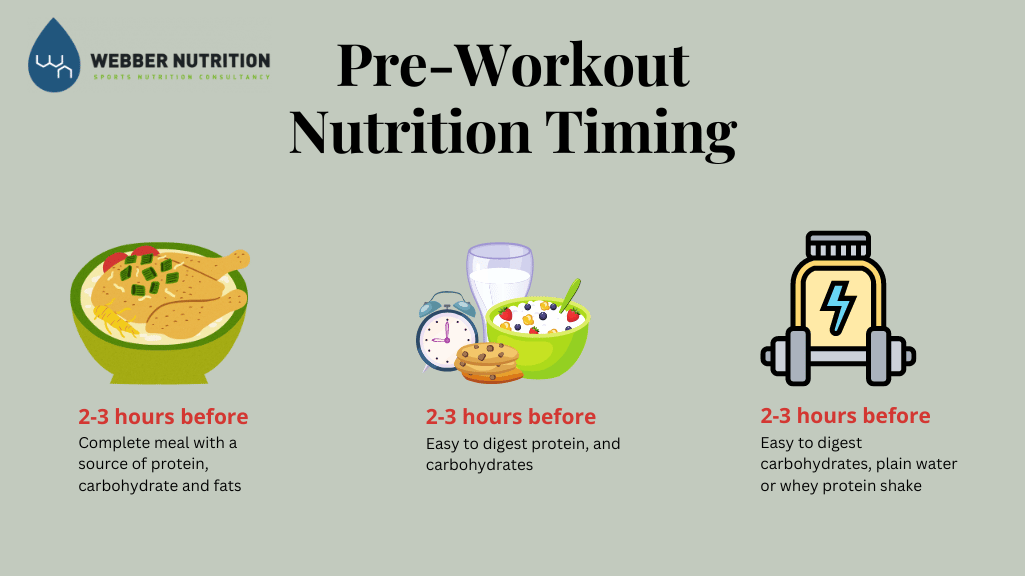
Pre-Workout Nutrition Timing
Knowing when you eat your pre-workout breakfast is very important. Professionals suggest that you eat 2-3 hours before a workout. Try to eat enough carbohydrates, protein, and fat-rich foods. This is important for longer and endurance exercise.
Consuming performance meals too close to a workout can cause discomfort while exercising. If you eat 45-60 minutes before the training, remember that if you are taking decent food that is easy to digest and contains enough carbs and protein.
It’s important to know that everyone is different and that what worked for one won’t work for others. It’s best to consult experts.
Pre-Workout Supplements
Supplements are often recommended before, after, and while a workout. But the riddle of when to take supplements remains unsolved. Pre-workout supplements are designed to give you endurance throughout the activity and reduce fatigue.
The supplements can be taken before a workout or while exercising. However, it is important to consult a nutritionist for safety.
1. Caffeine
Caffeine, a stimulant, can enhance energy, focus, and endurance during exercise. It functions by stimulating the nervous system, which may increase alertness and a brief increase in metabolic rate. You can exercise for longer amounts of time as a result of this. Additionally, coffee can aid in promoting the release of some hormones, such as adrenaline, which can improve muscle contractions and raise the body’s capacity to burn fat. Individual tolerance for caffeine varies; therefore, it’s crucial to remember that one should start with a low quantity and gradually increase it to find the ideal amount for them. Additionally, it’s important to remember that consuming too much caffeine can have unfavorable side effects like anxiety and insomnia.
2. Creatine
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound in some foods, including fish and red meat. Additionally, it is available in supplement form. Phosphocreatine, stored as creatine in the muscles, creates energy during high-intensity, swift-paced exercises like weightlifting and sprinting.
Creatine supplements can increase the muscle’s phosphocreatine reserves which induces the outcome of the exercise. It is possible to perform better during these types of activities. It has been demonstrated that creatine increases muscular endurance, strength, and power while encouraging muscle growth. Creatine also decreases fatigue and muscle injury.
When taken in the recommended doses, creatine is considered a safe supplement. It is crucial to remember that it could result in weight gain because the muscles retain water. Additionally, some people may have diarrhea or stomach discomfort after taking creatine for the first time. Always consult a nutritionist before you go all out in these supplements.
3. Chocolate Milk
Protein and carbohydrates found in chocolate milk can improve muscle repair after exercise and help with energy production. While the protein in chocolate milk can help develop and repair muscle tissue, carbohydrates can fuel your muscles while you work out. In addition, chocolate milk provides additional vital minerals, including calcium, potassium, and vitamin D, which are very important for overall health and might benefit athletes.
According to research, drinking chocolate milk as pre-workout nutrition can be useful to refill your glycogen levels, enhancing your performance and endurance. Due to the electrolytes it contains, it is also beneficial for recovery and rehydration.
Also, Learn more about why do athletes take protein supplements
Hydration Before Workout
Water is the best fluid to drink before a workout. Hydrating your body with enough liquid will reduce fatigue and help you reach the performance peak.
You can lose electrolytes via sweat, for which you can take sports drinks. Hydrating yourself with a sports drink can be beneficial if you are working out for more than an hour.
Consult a registered SENr Nutritionist
You can find quality blogs and forums from experts and nutritionist to develop and increase your physiques level but still you’ll retain some gaps. What you can do instead is consult a nutritionist in person to get accurate and safe advice on nutrition.
Nutritionists are licensed professionals who keeps you up-to-date according to your body’s requirements. A registered nutritionists can help you reach your goal with accurate feeding and exercises. Consult to a registered SENr nutritionist today.
FAQs
What foods give a good pump during exercise?
An easily digested, high-carbohydrate, and moderate protein meal is ideal before exercise to maximise energy levels. Some examples include porridge with banana and honey, a bagel with jam & peanut butter, or a homemade protein bar.
Are bananas good pre-workout?
Yes, bananas are good pre-workout snacks. They are rich in easy-to-digest carbohydrates and electrolytes that will support muscle function.
Should I eat anything before a workout?
Unless you’re training at a low intensity to be done deliberately before eating first thing in the morning, then yes, you should definitely look to eat something before training to give you better energy levels to work harder.
Can I work out on an empty stomach?
You can work out on an empty stomach, but your energy levels and recovery will be compromised compared to if you include a light pre-training snack e.g. banana.
What should I eat 30 minutes before a workout?
When eating just 30 mins or less before training, sticking to a very simple carbohydrate snack is the best option. Some examples include a banana, crumpet with jam, handful of dried fruit, glass of apple juice.